Kraków 2026-01-15

Steam Locomotive Oi1.
The Oi1 steam locomotive was produced between 1902 and 1910 by the Hohenzollern, Schwartzkopff, Hanomag, Henschel, and Karlsruhe factories. The Oi1 locomotive is the Polish designation for a Germanic steam locomotive designated the P6 series. The prototype was built in 1902. Between 1905 and 1910, 275 units of this locomotive were produced. Three locomotives were intended for military use. From the outset, the locomotive was designed to run on superheated steam, according to a design by engineer Robert Garbe from 1901. The goal was to create a universal steam locomotive for passenger and light freight traffic. In 1905, the locomotive received the P6 series designation. Individual factories built the following locomotives: Schwartzkopff 114, Hanomag 90, Henschel 37, Humboldt 25, Hohenzollern 5, and MBG Karlsruhe 4.
After the end of the Great War, the rebirth of the Polish Republic, and the establishment of the Polish State Railways (PKP), 44 locomotives were transferred to the Polish State Railways. They were donated to Poland as war reparations. They received designations from Oi1-1 to Oi1-44. P6 series locomotives were also sent to Belgium, France, Italy, Lithuania, Latvia, and other countries. After World War II, PKP had 31 Oi1 series locomotives in service until 1972.
The only preserved P6 series steam locomotive in Europe (ex-BR 37 171) was located at the Railway Museum in Warsaw and was later transported to the Museum in Kościerzyna.
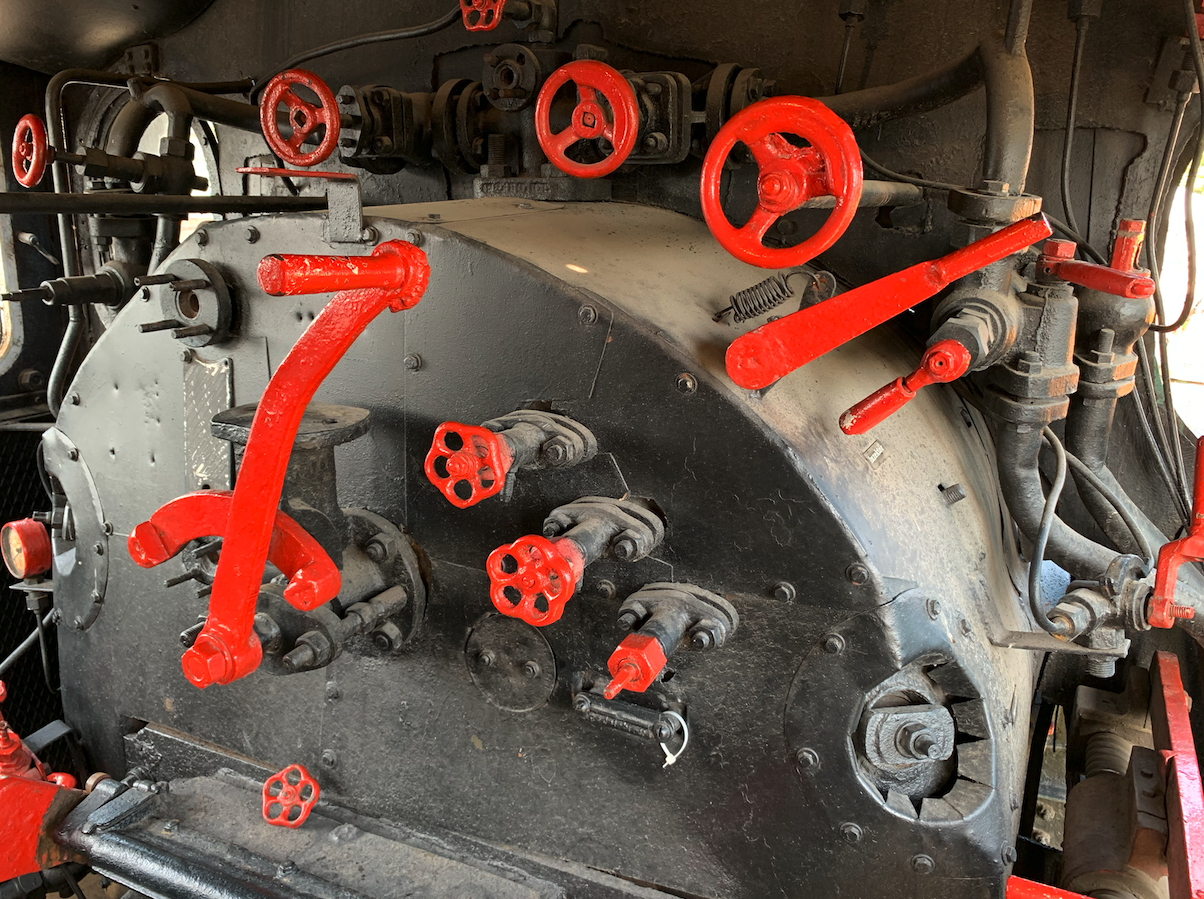
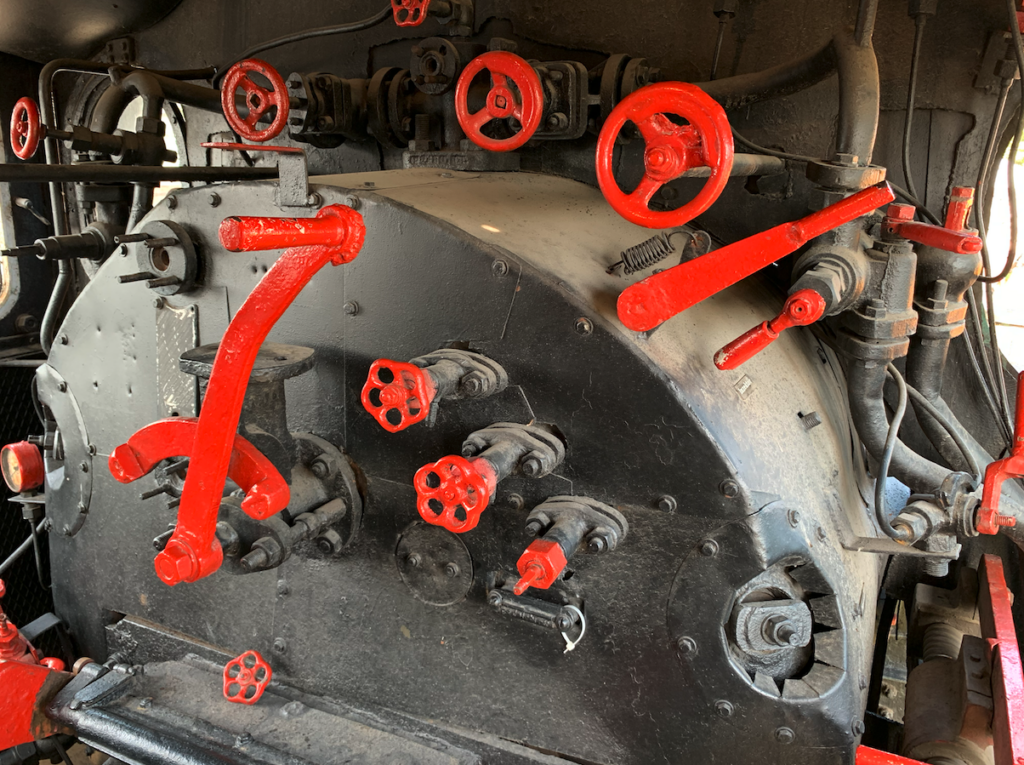
The locomotive has a 1’C axle arrangement. The locomotive weighs 57,100 kg. The operating weight is 100,100 kg. Length is 10.508 m. Length with tender is 17.958 m. Diameter of driving wheels is 1.60 m. Diameter of rolling wheels is 1.00 m. Boiler pressure is 12 atmospheres. Boiler heating area is 131.58 m². Superheater area is 3.90 m². Grate area is 2.28 m². Cylinder diameter is 0.54 m. Piston stroke is 0.30 m. Tender type is 16D1. Design speed is 70-90 km/h.
Steam locomotive Oi1-29. The locomotive was manufactured by Berliner Maschinenbau AG, vormals L. Schwartzkopff (BMAG). Serial number 3450. Year of manufacture 1905. Design speed 75 km/h. Steam pressure 12 atmospheres. Drive wheel diameter 1.60 m. Rolling wheel diameter 1.00 m. Tender type 16D1; it could carry 16 m3 of water and 5,000 kg of coal. Service weight with tender is 100,100 kg. Length over buffers 17.958 m.
The maximum design speed of the P6 locomotive was 90 km/h. The maximum axle load was 15,200 kg. The locomotives also used drive wheels with a diameter of 1.55 m. Other steam engines were also used, with a smaller diameter of 520 mm. In the prototypes, the superheater heating area was smaller, at 32 square meters.
Steam Locomotive Oi2.
The steam locomotive Oi2 was produced from 1927 to 1940. The locomotives were manufactured at the Schichau, Henschel, and Hanomag factories. The locomotive was built at the request of the German Ministry of Railways in 1924. The Baureihe 24 series passenger locomotives were designed to haul passenger trains on local lines and light freight trains. The first locomotive was commissioned for testing in February 1928. The German Railways ordered 90 locomotives. The design was developed in 1925. Production began in 1927 at the Schichau plant in Elbląg. In February 1928, the first example of the new series entered regular service. In 1928, production of these locomotives began in Wrocław at the Linke-Hofmann company, and later at other German factories. In the first two years, 63 locomotives of the 24 series were built. Production was halted due to the global economic crisis.
Axle configuration: 1C h2. Locomotive weight: 73,800 kg. Service weight: 100,800 kg. Length 10.12 m. Length with tender 16.995 m. Height 4.165 m. Wheelbase 13.27 m. Drive wheel diameter 1.50 m. Rolling wheel diameter 0.85 m. Boiler with pressure 14 atmospheres. Boiler heating area 105.4 m2. Superheater area 37.2 m2. Grate area 2.04 m2. Cylinder diameter 500 mm. Piston stroke 660 mm. Design speed 90 km/h. Tender type 16C1. Capacity of water 16 m3. Capacity of hard coal 5,000 kg.
The first BR 24 locomotives were assigned to the locomotive depots of Wriezen, Neustettin (Szczecinek), and Schwerin in Pomerania and Mecklenburg. Ultimately, the locomotives were operated in many regions of Germany. During World War II, German forces assembled most of the BR 24 locomotives in Pomerania and East Prussia, serving the military and manufacturing plants.
After World War II, BR 24 locomotives were deployed in Poland at the locomotive depots of Kołobrzeg, Iława, Szczecinek, Malbork, and Olsztyn. After World War II, the Polish State Railways (PKP) acquired the BR 24 locomotives from these areas, which they designated Oi2. There were 43 of these locomotives in service, and they were used for passenger and light freight trains. In the autumn of 1946, 31 locomotives were in service with the Polish State Railways (PKP): 20 in the Gdańsk Directorate and 11 in the Szczecin Directorate. At the turn of 1946/1947, these locomotives were designated the Oi2 series. By October 1948, all of these locomotives were stationed in the Gdańsk Directorate, and 24 of them were operational. Several damaged locomotives were removed from the inventory before new numbers were assigned.
Over the next 50 years, these locomotives underwent minor modifications. The steam superheaters were removed. The smokebox doors were changed from convex to flat, and the central locking mechanism was replaced with a bolted type. The air compressors and compressed air tanks were replaced. The accessories were replaced with Polish-made accessories.
With the ongoing electrification, the Oi2 locomotives were relocated to local routes and shunting duties. In 1974, the Oi2 locomotives were concentrated in the Inowrocław and Zajączkowo Tczewskie depots. The last Oi2 locomotive was decommissioned in October 1976. The decision was made to preserve the locomotive as a technical monument.
The locomotive was equipped with an Ackermann safety valve. A Knorr superheater was installed in front of the chimney. The locomotive was equipped with Wagner windchests and Knorr brakes. The vehicle has a steam exhaust system for heating the passenger cars.
Written by Karol Placha Hetman